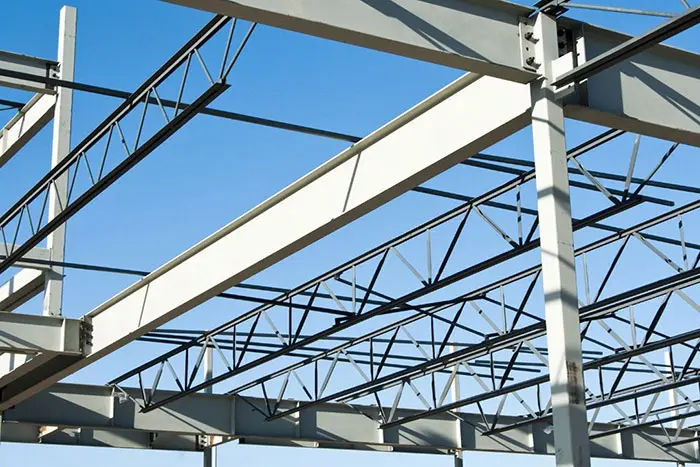
The Role of CAD in Structural Steel Processing
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) has revolutionized the way structural steel is processed, designed, and fabricated in the construction industry. CAD software offers powerful tools and functionalities that significantly enhance productivity, precision, and collaboration throughout the entire steel processing workflow. In this article, we will explore the critical role of CAD in structural steel processing and its impact on the industry.
CAD in structural steel processing
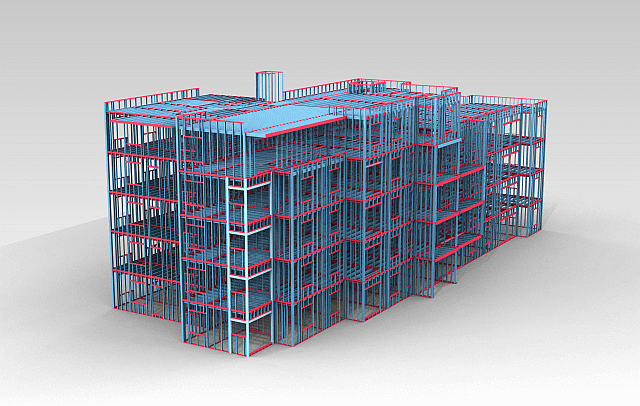
- Efficient Design and Drafting: CAD in structural steel processing enables engineers and designers to create detailed 2D and 3D models of structural steel components. The software provides an intuitive interface, advanced drafting tools, and libraries of pre-built steel elements, making the design process faster and more accurate. CAD allows for precise dimensioning, annotation, and documentation, ensuring that every aspect of the steel structure is captured.
- Simulation and Analysis: CAD software offers simulation and analysis capabilities that allow engineers to evaluate the structural performance of steel components. Finite element analysis (FEA) tools integrated into CAD platforms enable engineers to simulate load-bearing scenarios, assess stress distribution, and optimize designs for strength and stability. This helps in identifying potential issues early on and ensures that the final steel structure meets safety and performance requirements.
- Material Optimization: CAD in structural steel processing assists in material optimization by providing tools to analyze and optimize the use of structural steel. Engineers can evaluate different design options, explore alternative shapes and configurations, and identify opportunities to reduce material waste. By minimizing material usage without compromising structural integrity, CAD helps reduce costs and supports sustainable construction practices.
- Clash Detection and Coordination: CAD software facilitates clash detection and coordination between different building systems. It allows for the integration of various disciplines, including architectural, structural, and MEP (mechanical, electrical, and plumbing) systems, ensuring that all components fit together seamlessly. Clash detection tools identify potential conflicts or interferences between different elements, enabling prompt resolution before construction begins.
- Accurate Fabrication Drawings: CAD software generates precise fabrication drawings from the 3D models, providing fabricators with accurate instructions for manufacturing steel components. The software automatically generates detailed shop drawings, including dimensions, material specifications, weld symbols, and assembly instructions. This streamlines the fabrication process, reduces errors, and improves the overall quality of the fabricated steel elements.
- CNC Integration: CAD in structural steel processing seamlessly integrates with Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machinery used in structural steel processing. The 3D models created in CAD can be directly translated into machine instructions for cutting, drilling, and shaping steel components with high precision. This integration minimizes manual measurements, reduces human error, and improves efficiency and accuracy in the fabrication process.
- Collaboration and Communication: CAD software enhances collaboration and communication among project stakeholders. Design teams, architects, engineers, fabricators, and contractors can access and work on the same CAD models, making real-time changes, annotations, and comments. This fosters effective communication, streamlines decision-making, and ensures that everyone is working with the latest design information.
- Project Visualization: CAD in structural steel processing provides visual representations of the steel structure, helping stakeholders visualize the final product. Photorealistic renderings and 3D visualizations enable clients, investors, and project teams to understand the design intent better and make informed decisions. Visualization tools assist in conveying the architectural vision, evaluating design alternatives, and facilitating project approvals.
- Design Variations and Iterations: CAD software allows for easy exploration of design variations and iterations. Engineers can quickly modify parameters, adjust dimensions, or experiment with different configurations to find the optimal solution. This iterative design process helps in refining the structural steel components, improving their performance, and meeting specific project requirements.
- Documentation and Project Management: CAD in structural steel processing streamlines the documentation process by automatically generating detailed drawings, bills of materials, and specifications. This ensures accuracy and consistency in the documentation, saving time and reducing errors. Additionally, CAD tools can be integrated with project management software, allowing for better coordination, scheduling, and tracking of steel processing tasks.
- Quality Control and Inspection: CAD software plays a crucial role in quality control and inspection during structural steel processing. It enables engineers to create inspection checklists, define tolerance limits, and compare as-built components with CAD models. This helps in identifying any deviations or errors, ensuring compliance with design specifications and quality standards.
- Retrofitting and Renovation: CAD software aids in retrofitting and renovation projects by providing precise measurements and accurate 3D models of existing structures. Engineers can use these models to assess the feasibility of modifications, plan new structural elements, and ensure seamless integration with the existing steel framework. This facilitates efficient and cost-effective retrofitting solutions.
- Training and Education: CAD in structural steel processing serves as a valuable tool for training and education in the field of structural steel processing. It allows students, engineers, and technicians to learn and practice drafting, modeling, and design techniques. CAD software offers a hands-on approach, enabling learners to simulate real-world scenarios and gain practical experience in creating 3D models for structural steel components.
- Continuous Improvement and Innovation: CAD in structural steel processing companies continually invest in research and development to enhance their products. This leads to the introduction of new features, advanced analysis capabilities, and improved integration with other software and technologies. Structural steel processors can benefit from these continuous improvements and stay updated with the latest tools and techniques to optimize their operations.
Computer-Aided Design in Structural Steel Processing
CAD in structural steel processing plays a vital role in structural steel processing by providing robust design and drafting tools, simulation capabilities, clash detection, and collaboration features. The software streamlines the design process, enhances precision, reduces errors, and facilitates effective communication among project stakeholders. As the construction industry continues to evolve, CAD will remain an essential tool for optimizing structural steel processing, improving productivity, and delivering high-quality steel structures.