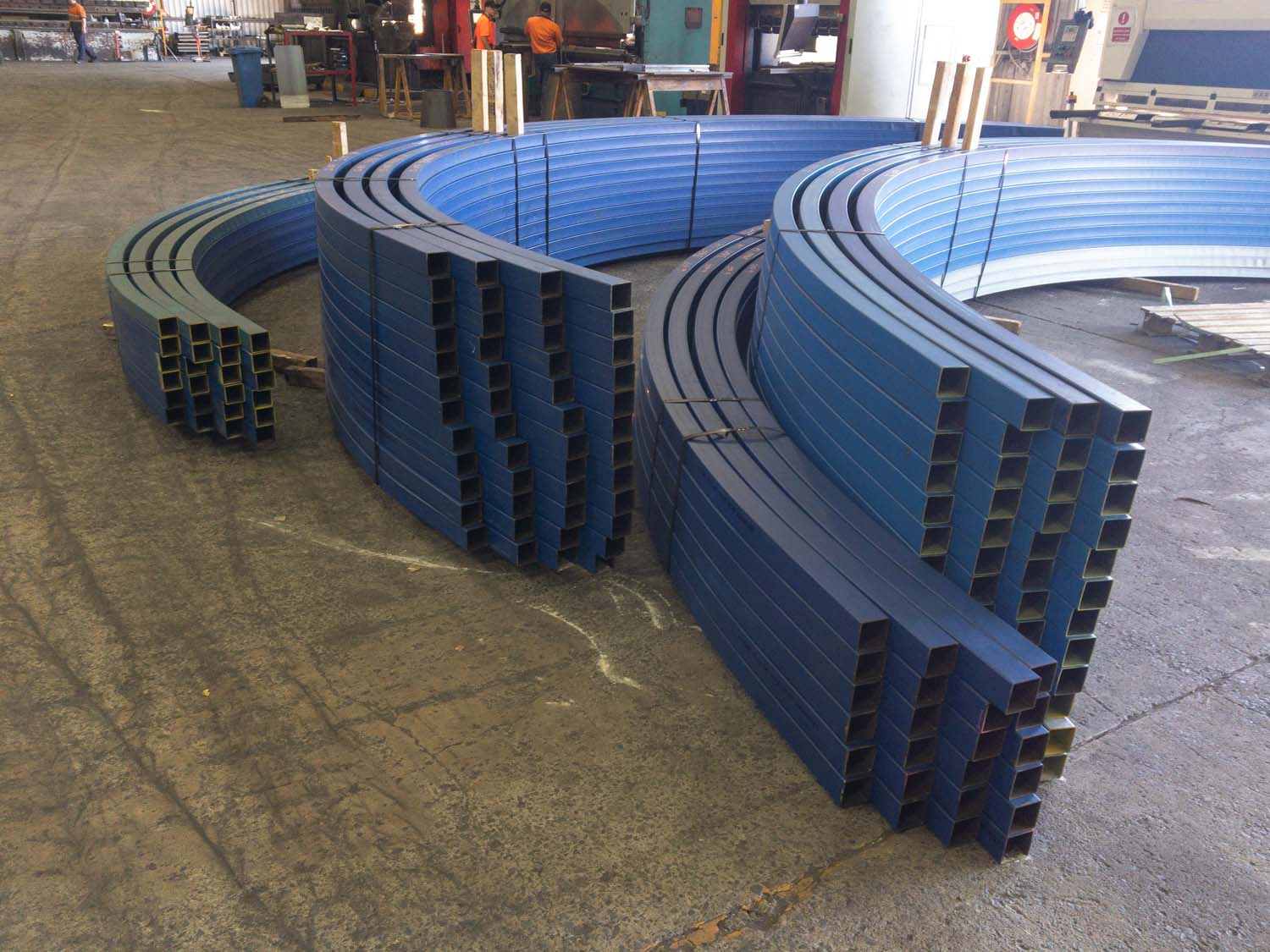
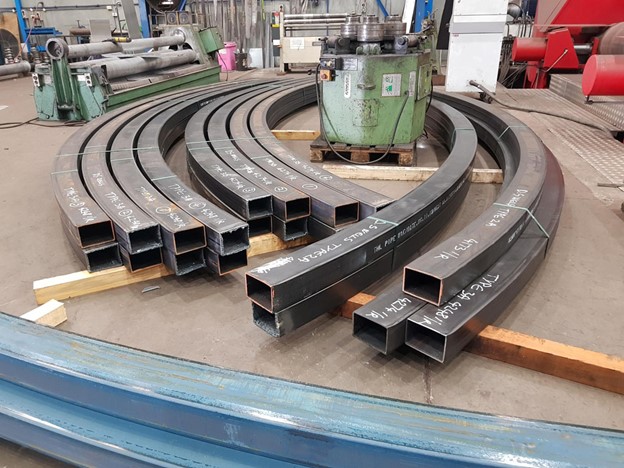
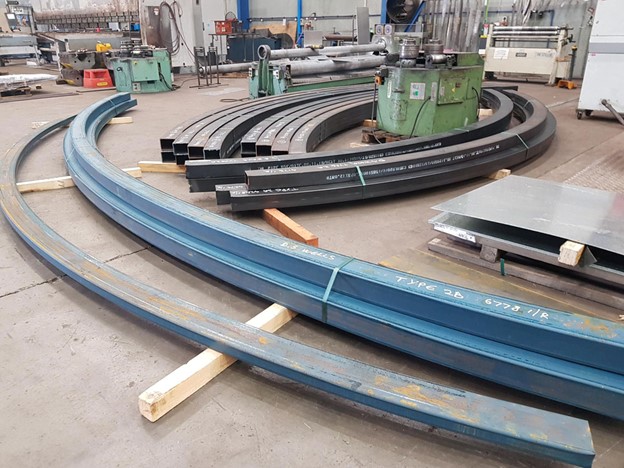
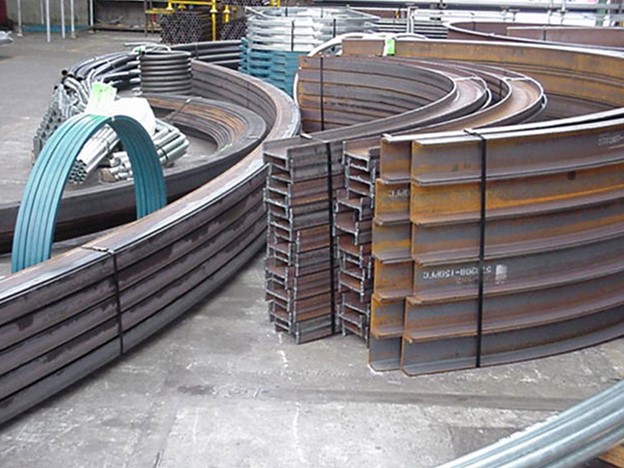
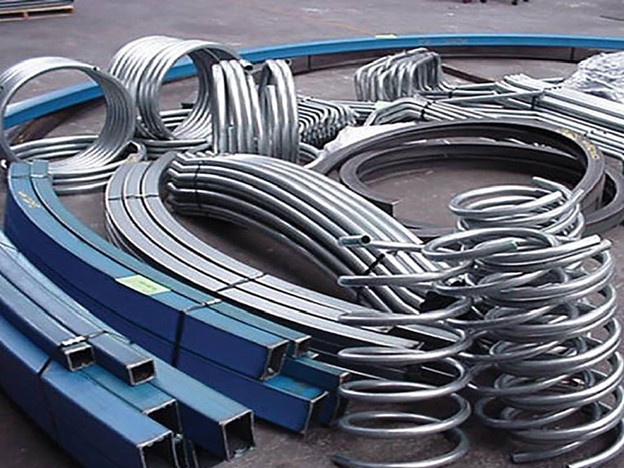
Understanding Different Section Rolling Techniques: Hot Rolling vs. Cold Rolling

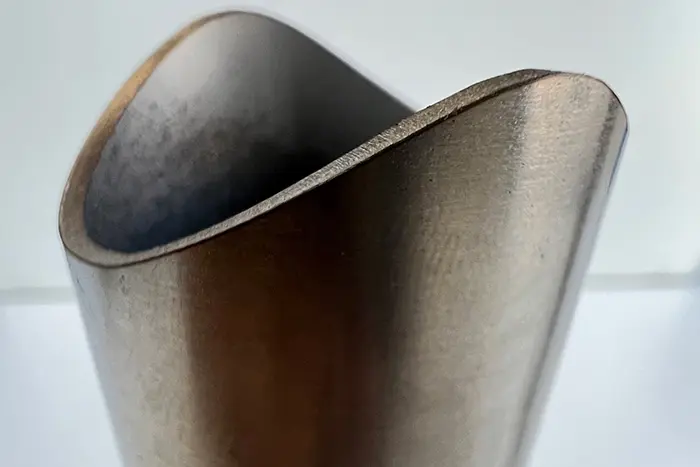
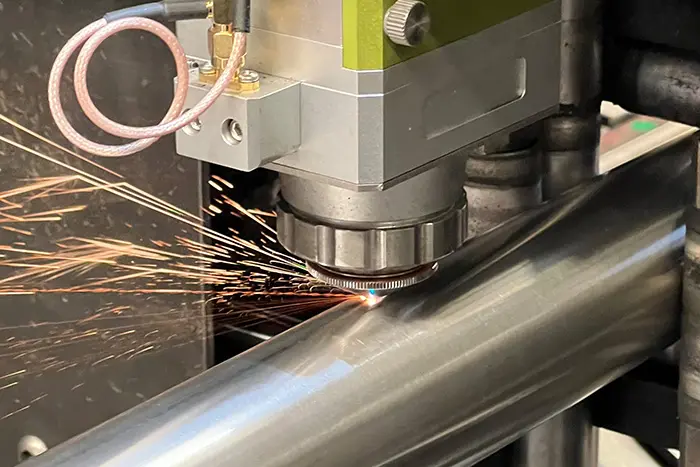
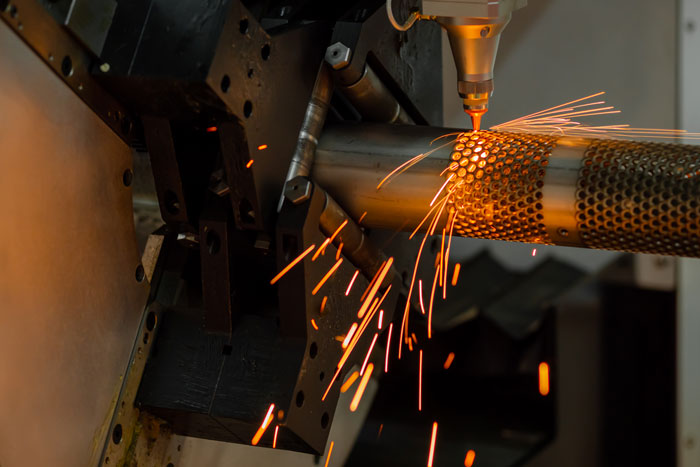
Section Rolling Techniques is a crucial process in the manufacturing industry that involves shaping and forming various sections, such as beams, channels, and angles, from different materials. Two common techniques used in section rolling are hot rolling and cold rolling. Each technique offers distinct advantages and is suited for specific applications. In this article, we will explore the differences between hot rolling and cold rolling, their benefits, and their applications.
Hot Rolling
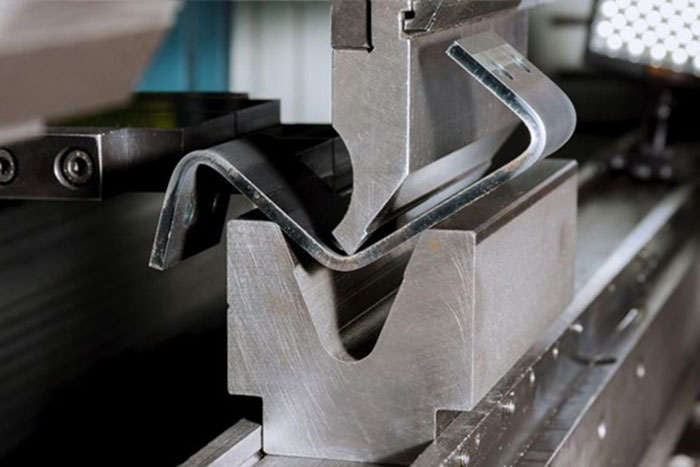
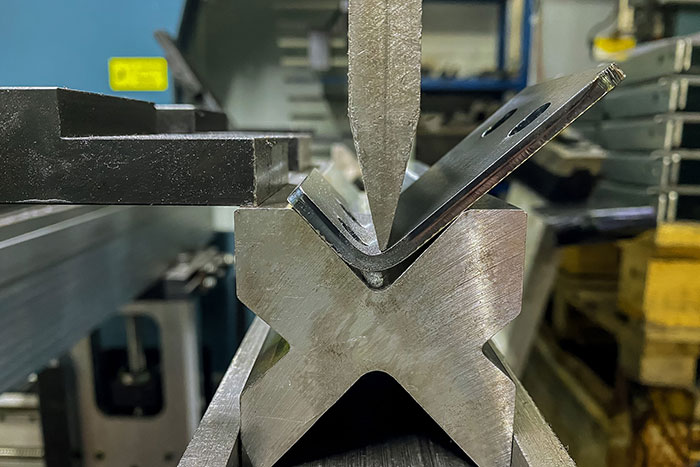
Hot rolling is a section rolling technique that involves heating the material above its recrystallization temperature and then passing it through a series of rollers to achieve the desired shape. Here are some key features and benefits of hot rolling:
- Plastic Deformation: The material becomes more malleable due to the elevated temperature, allowing for significant plastic deformation. This enables the production of larger sections with complex shapes.
- Grain Refinement: The high temperature during hot rolling promotes grain refinement, resulting in improved mechanical properties, such as enhanced strength and toughness.
- Cost-Efficient: Hot rolling is generally more cost-effective compared to cold rolling because it requires less energy and reduces the need for subsequent heat treatments.
- Wide Range of Materials: Hot rolling is suitable for a wide range of materials, including steel, aluminum, and other alloys.
Hot rolling finds applications in various industries, such as construction, infrastructure, and automotive. It is commonly used for manufacturing structural components, rails, pipes, and large-sized sections.
Cold Rolling
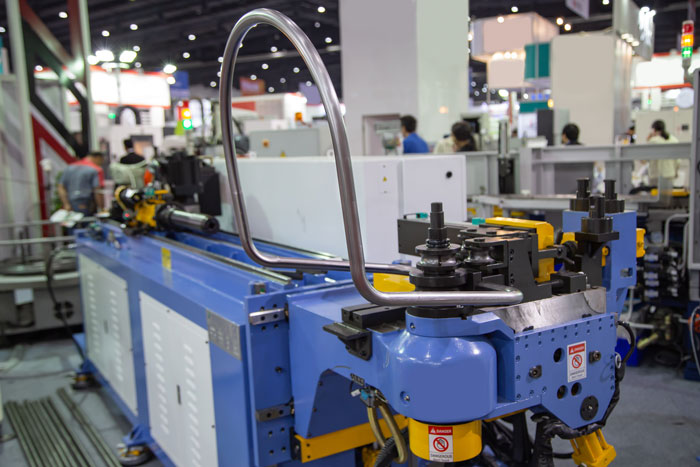
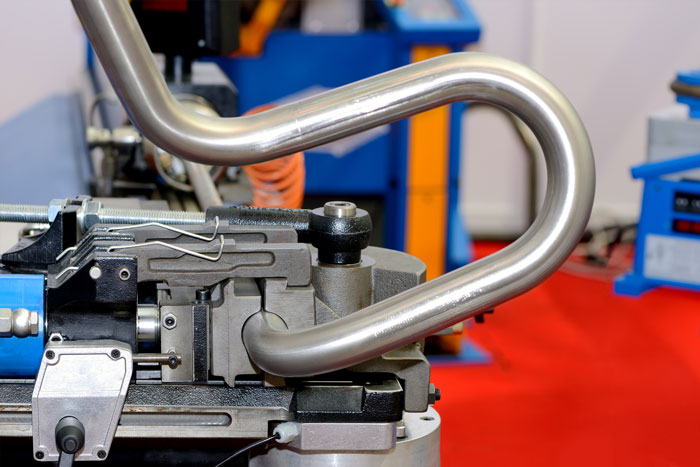
Cold rolling is a section rolling technique. as the name suggests, it involves rolling the material at room temperature or slightly below. Unlike hot rolling, cold rolling does not involve heating the material. Let’s explore the advantages and applications of cold rolling:
- Improved Dimensional Accuracy: Cold rolling produces sections with excellent dimensional accuracy, smooth surfaces, and tight tolerances, making it ideal for applications that require precise measurements.
- Increased Strength and Surface Hardness: Cold rolling work hardens the material, resulting in increased strength and surface hardness. Cold-rolled sections exhibit improved mechanical properties and better resistance to deformation.
- Surface Finish: Cold rolling offers a superior surface finish, making it suitable for applications where aesthetics and surface quality are important.
- Thin and Lightweight Sections: Cold rolling is well-suited for producing thin and lightweight sections with high precision. It is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
Cold rolling is widely employed in the production of sheet metal, strips, tubes, and precision components that require dimensional accuracy, high strength, and superior surface finish.
Choosing the Right Technique
The choice between hot rolling and cold rolling in Section Rolling Techniques depends on several factors, including the material properties, required section size and shape, cost considerations, and the intended application. It is crucial to consider these factors and consult with experts to determine the most appropriate technique for specific projects.
In addition to the advantages mentioned above, it is important to consider the environmental impact of section rolling techniques. Sustainable practices and material waste reduction play a significant role in minimizing the environmental footprint of section rolling processes. Here are some key considerations:
- Material Efficiency: Efficient material usage is crucial to reduce waste and minimize environmental impact. Proper planning and optimization of section dimensions can help maximize material utilization and minimize scrap.
- Recycling and Reusing: Implementing recycling and reuse programs for metal scrap and waste generated during section rolling can significantly reduce the environmental impact. Recycling not only conserves natural resources but also reduces energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with the production of new materials.
- Energy Efficiency: Energy-intensive processes like section rolling can contribute to a significant carbon footprint. Implementing energy-efficient practices, such as using advanced equipment, optimizing process parameters, and employing energy-saving technologies, can help reduce energy consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
- Emissions Control: Implementing effective emission control measures, such as proper ventilation systems and filtering technologies, can minimize air pollution and improve the air quality in the surrounding environment.
- Compliance with Regulations: Adhering to environmental regulations and standards is essential to ensure responsible and sustainable section rolling operations. Compliance with emissions limits, waste disposal guidelines, and other environmental regulations helps protect the environment and mitigate potential risks.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular assessment and monitoring of environmental performance are essential to identify areas for improvement. Implementing measures to reduce waste generation, increase recycling rates, and improve energy efficiency can lead to ongoing environmental progress.
By adopting sustainable practices and minimizing material waste, the Section Rolling Techniques and industry can contribute to a more environmentally friendly and responsible approach to manufacturing. Collaborative efforts between manufacturers, industry organizations, and regulatory bodies can drive the development and implementation of sustainable solutions for section rolling processes.
Section Rolling Techniques
section rolling techniques, such as hot rolling and cold rolling, offer distinct benefits in terms of shaping and forming various sections. However, it is essential to consider the environmental impact of these processes. By focusing on sustainable practices, material efficiency, energy conservation, and emissions control, the section rolling industry can reduce its environmental footprint and contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.
Both hot rolling and cold rolling are essential section rolling techniques with unique advantages. Hot rolling offers greater plastic deformation and is suitable for large sections, while cold rolling provides superior dimensional accuracy, increased strength, and excellent surface finish. Understanding the differences between these techniques helps manufacturers make informed decisions and achieve optimal results in their section rolling processes.