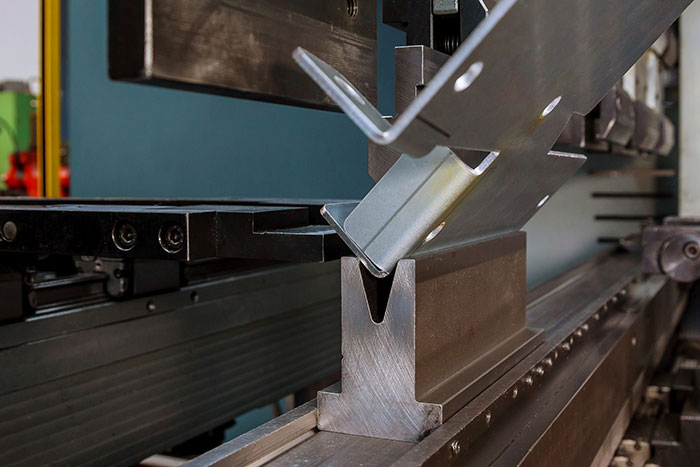
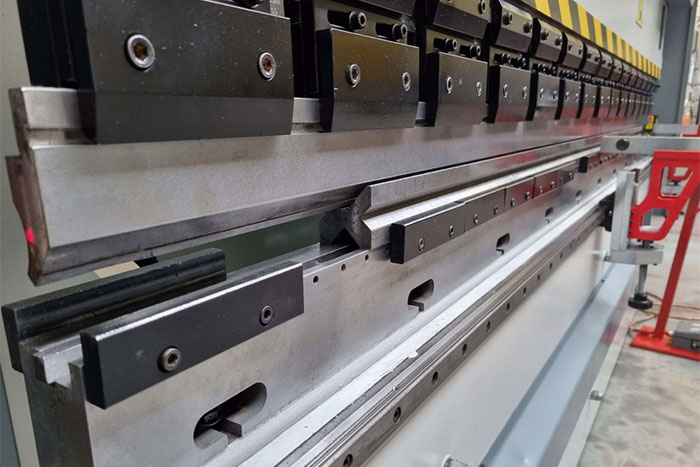
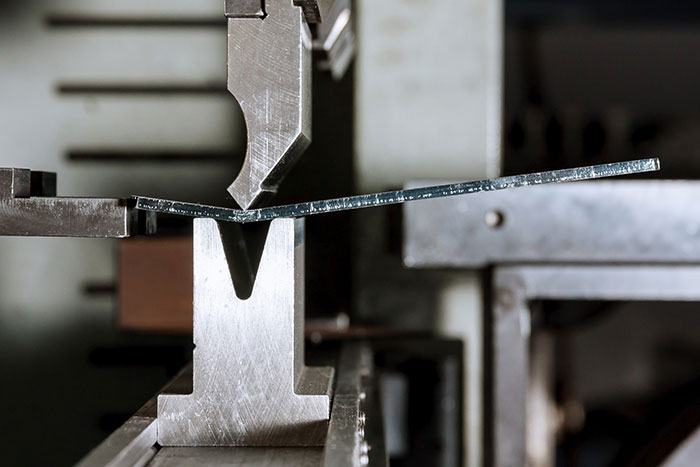
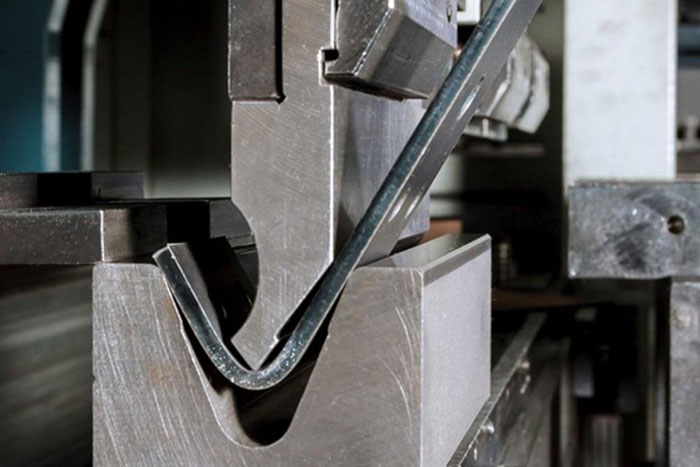
The Basics of Flat Laser Cutting: An Introduction to the Process and Its Applications
In the world of manufacturing and fabrication, flat laser cutting has emerged as a highly efficient and precise method for cutting various materials with exceptional accuracy. This article serves as a comprehensive introduction to the basics of flat laser cutting, exploring its process, components, and applications. Understanding the fundamentals of this technology will provide valuable insights into its capabilities and potential benefits in a wide range of industries.
An Introduction to the Process and Its Applications
- What is Flat Laser Cutting?
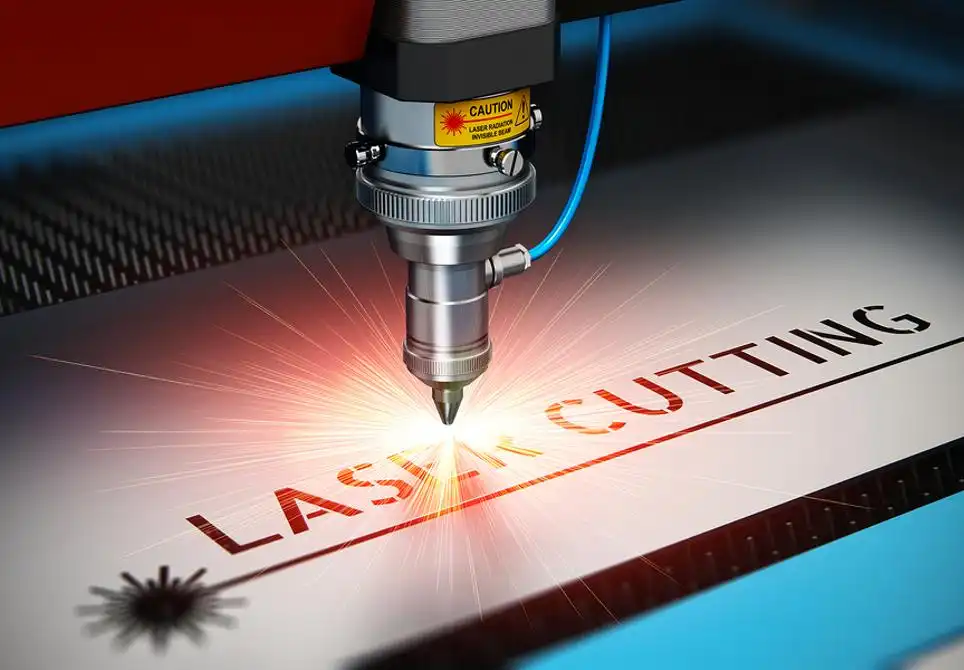
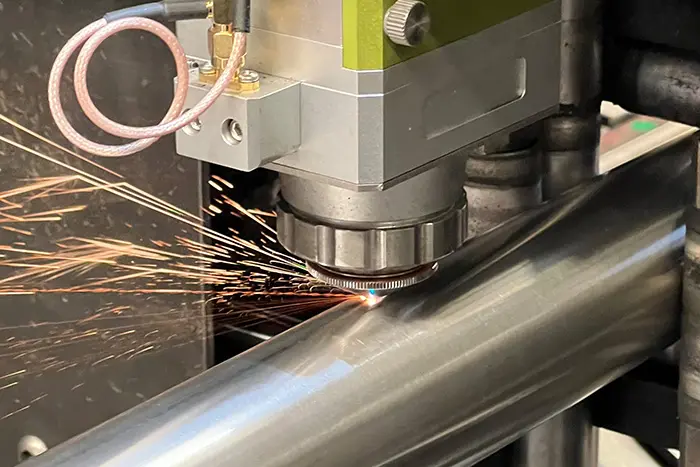
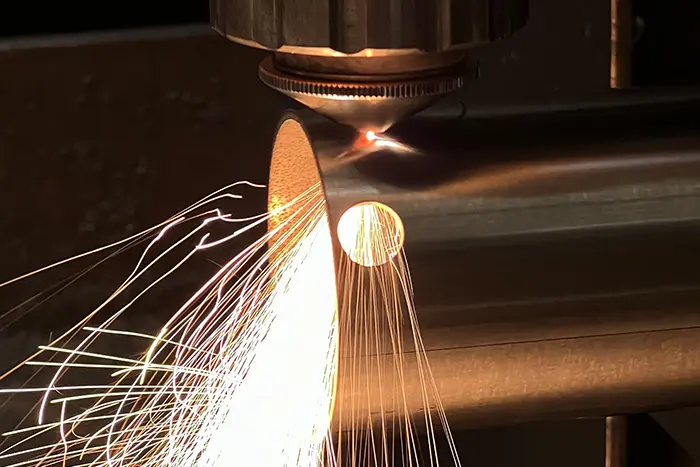
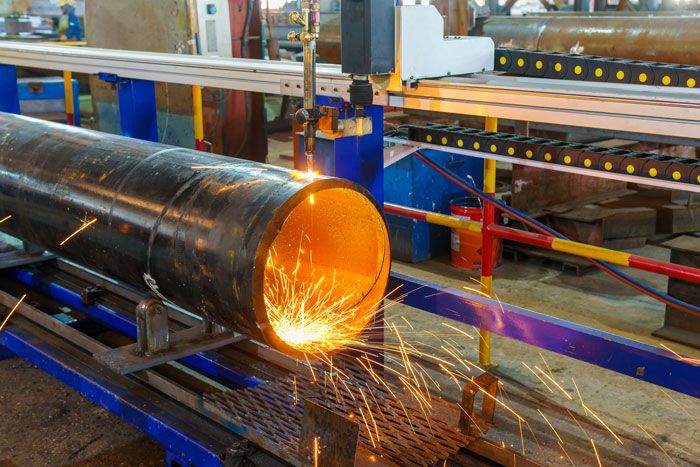
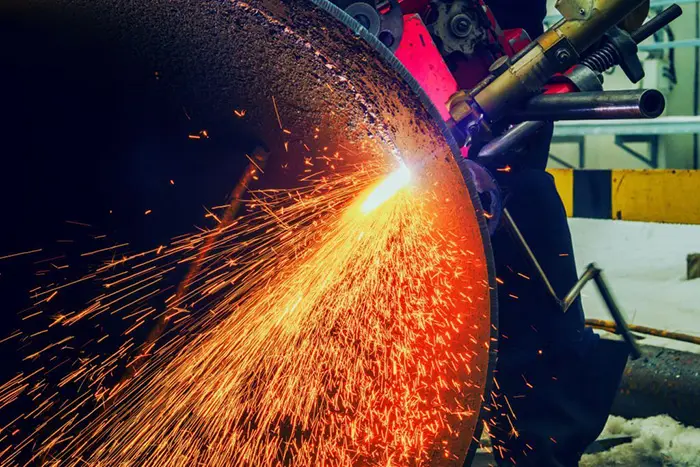
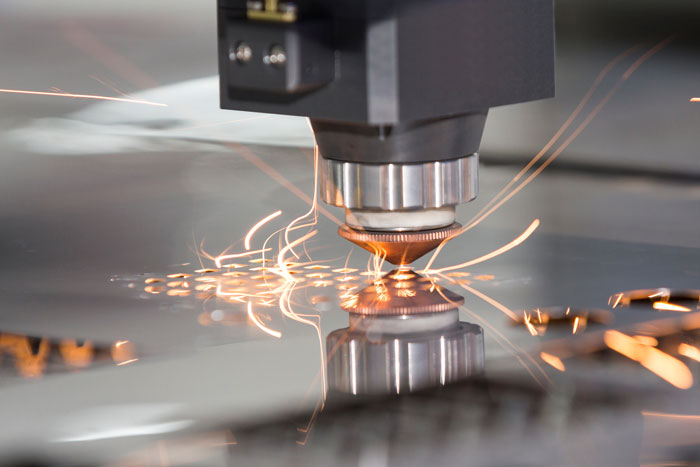
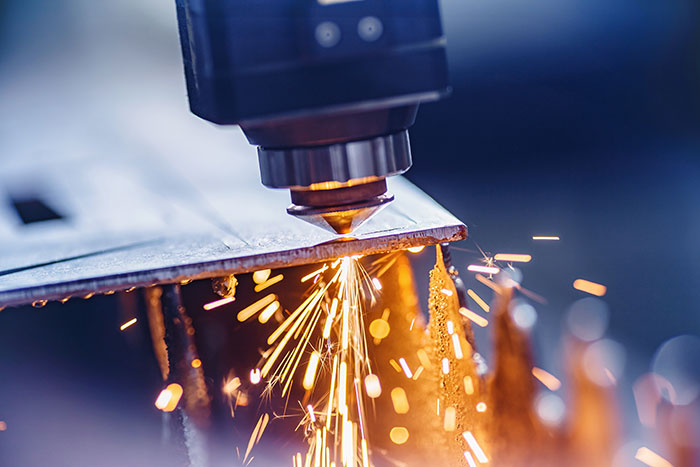
The Basics of Flat Laser Cutting is a non-contact cutting process that utilizes a highly focused laser beam to cut through a variety of flat sheet materials with precision. The laser beam is generated by a laser source and directed onto the material’s surface, melting or vaporizing the material along the predefined cutting path.
- How Does Flat Laser Cutting Work?
Flat laser cutting involves several key components:
a. Laser Source: The laser source emits a high-intensity laser beam, typically generated through the excitation of a laser medium such as carbon dioxide (CO2), fiber, or solid-state lasers.
b. Optics System: The optics system consists of mirrors and lenses that guide and focus the laser beam onto the material’s surface with high accuracy.
c. CNC Control System: A computer numerical control (CNC) system controls the movement of the laser cutting machine, following the pre-programmed cutting path to achieve precise cuts.
d. Assist Gas: In many cases, an assist gas, such as oxygen or nitrogen, is used to enhance the cutting process by blowing away molten material and ensuring clean, precise cuts.
- Applications of Flat Laser Cutting:
The Basics of Flat Laser Cutting finds applications across various industries, including:
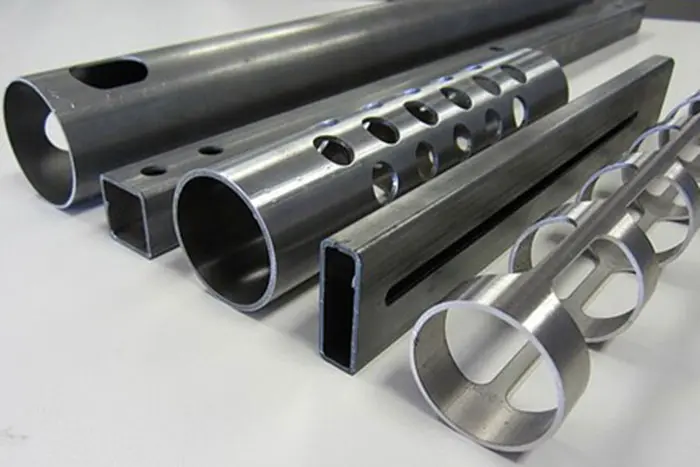
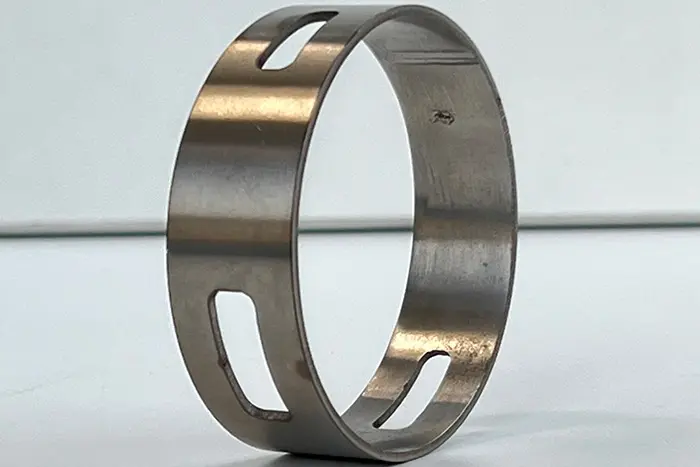
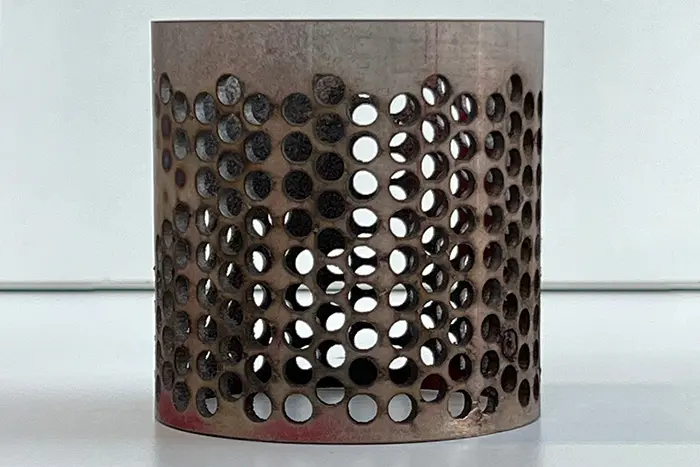
a. Metal Fabrication: Flat laser cutting is widely used in the metal fabrication industry for cutting materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, mild steel, brass, and copper. It is employed to create intricate shapes, precise edges, and complex geometries required in industries like automotive, aerospace, and architecture.
b. Signage and Advertising: The precision and versatility of flat laser cutting make it an ideal choice for cutting letters, logos, and intricate designs in materials like acrylic, wood, foam, and plastics used in signage and advertising applications.
c. Electronics and Consumer Goods: Flat laser cutting is utilized in the production of electronic components, circuit boards, and consumer goods. Its ability to create precise, clean cuts enables the fabrication of intricate designs, small parts, and intricate patterns required in these industries.
d. Textiles and Leather: Flat laser cutting offers precise and clean cuts in textiles and leather materials, facilitating the production of custom apparel, footwear, upholstery, and accessories.
- Advantages of Flat Laser Cutting:
The Basics of Flat Laser Cutting offer several advantages over traditional cutting methods, including:
a. High Precision: Flat laser cutting provides exceptional precision, allowing for intricate cuts, sharp edges, and complex geometries that would be challenging to achieve with other cutting methods.
b. Versatility: Flat laser cutting is compatible with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, textiles, and more. It enables the cutting of various thicknesses and sizes, accommodating diverse project requirements.
c. Speed and Efficiency: Flat laser cutting is a rapid and efficient process, reducing production time and increasing overall productivity.
d. Minimal Material Waste: The precise nature of flat laser cutting results in minimal material waste, maximizing material utilization and cost-effectiveness.
- Design Freedom: The Basics of Flat Laser Cutting allows for intricate and complex designs, offering designers unparalleled freedom and creativity. The ability to cut intricate patterns, detailed engravings, and fine contours enables the production of highly customized and visually appealing products.
- Non-Contact Process: One of the significant advantages of flat laser cutting is that it is a non-contact process. The laser beam does not physically touch the material being cut, minimizing the risk of material damage or deformation. This makes it suitable for cutting delicate materials that may be sensitive to pressure or physical contact.
- Automation and Integration: The Basics of Flat Laser Cutting machines can be integrated into automated production lines, improving efficiency and reducing labor costs. With the ability to connect to computer-aided design (CAD) software and robotics, flat laser cutting can be seamlessly integrated into the overall manufacturing process, streamlining workflows and improving overall productivity.
- Minimal Post-Processing: The precision and quality of cuts achieved through flat laser cutting often eliminate or minimize the need for extensive post-processing. This reduces the time, effort, and costs associated with additional finishing or machining operations.
- Enhanced Safety: Flat laser cutting machines are equipped with safety features to protect operators and ensure a safe working environment. Safety measures such as beam enclosures, safety interlocks, and emergency stop systems help prevent accidents and injuries during the operation.
- Sustainability: The Basics of Flat Laser Cutting is a sustainable cutting method due to its minimal material waste and energy efficiency. The precision of the cuts reduces material scrap, optimizing material usage and minimizing environmental impact. Additionally, the energy efficiency of laser-cutting machines contributes to reduced energy consumption and carbon footprint.
- Quality Control: The Basics of Flat Laser Cutting offers excellent control over the cutting process, resulting in consistent and high-quality cuts. This helps maintain product quality standards and reduces the likelihood of defects or rework.
- Maintenance and Service: Regular maintenance and servicing of flat laser cutting machines are essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Following manufacturer guidelines for maintenance schedules and performing routine inspections can help identify and address any issues promptly, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous operation.
The Basics of Flat Laser Cutting
Flat Laser Cutting is a highly versatile and efficient cutting process that offers exceptional precision and a wide range of applications across various industries. By harnessing the power of laser technology, this method enables the fabrication of complex designs, intricate patterns, and precise cuts in different materials. Understanding the basics of flat laser cutting and its advantages provides a solid foundation for exploring the potential of this cutting-edge technology in modern manufacturing and fabrication processes.